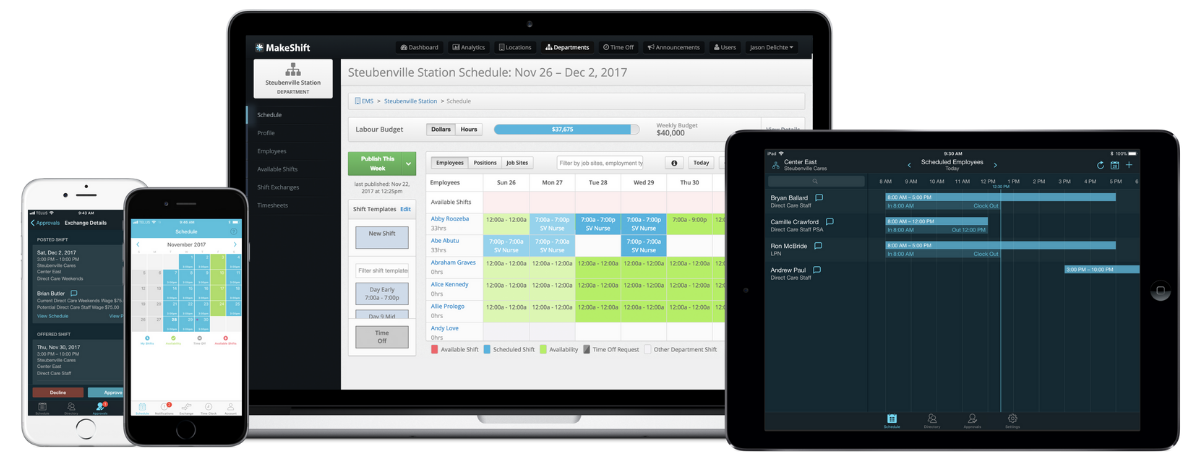
Picture this.
Your healthcare facility runs like butter in a hot skillet.
Your nursing staff is happy, fulfilled, and actually likes coming to work. Right this minute, your inbox has requests from highly-skilled nurses wanting a spot on your staff.
Your facility is known for exceptional patient care. (You’ve got the recognition and revenue to prove it.) Patients feel valued, heard, and well-cared for.
Sound good? You don’t have to answer that.
We know it does.
Now, a lot goes into turning that picture into reality. (And maybe having nurses beg you for a job is a bit of a reach, but still..)
One giant piece of the puzzle is choosing the right nursing staff model of care for your facility.
The right model prioritizes your staff and patients while factoring in how your facility operates best. When you adopt the right one, you’ll experience the sweet spot of holistic healthcare management.
Let’s talk about the 5 nursing staff models of care and how to choose the right one for you. If you’re already in the know on the WHAT & the WHY, skip to the 5 nurse staffing models and start there.
- What’s a Nurse Staffing Model, and Why is it Important?
- Why the Right Nurse Staffing Model of Care Is Crucial
- 5 Types of Nurse Staffing Models
- MakeShift Supports Multiple Nurse Staffing Models
- The Right Nursing Staff Model of Care Makes the Difference
What’s a Nurse Staffing Model, and Why is it Important?
Nurse staffing models are frameworks used to determine the allocation and distribution of nursing staff in healthcare settings.
These models aim to optimize patient care, manage workload, and ensure efficient utilization of nursing resources.
Each staffing model has pros and cons. Your model choice depends on patient needs, available resources, and organizational goals.
When you’re choosing the nurse staffing model for your facility, consider factors like:
- Workload
- Staff skill mix
- Staff experience
- The existing collaboration level among your nursing staff
Why Choosing the Right Nurse Staffing Model of Care Is Crucial
When you find the right staffing model of care for your operation — you’ll know it in how your facility runs.
- Top-tier patient care — A well-suited nurse staffing model ensures the correct number of nurses are available to provide safe and high-quality care to your patients. The right staffing model helps you maintain safe nurse-to-patient ratios — you already know how important this is.
- Workload management — Nurse staffing models factor in patient acuity, nurse-patient ratios, and workload distribution. By appropriately using nursing resources, a model of care helps prevent excessive workloads and burnout among your nurses. Adequate staffing levels allow your nurses to manage their responsibilities effectively, which eases stress and boosts retention.
- Resource utilization — A suitable nurse staffing model helps optimize your nursing resources. By matching nurses' number and skill mix with patient needs, you control costs AND deliver quality care. Effective resource utilization cuts down on overtime expenses and relying on temp staff.
- Regulatory compliance — Nurse staffing models help you meet regulatory requirements and industry standards. Many jurisdictions have guidelines or regulations to ensure adequate nurse staffing levels. Adhering to these standards helps avoid penalties and legal consequences while maintaining patient and staff safety.
- Staff satisfaction and retention — Adopting a fair and appropriate nurse staffing model of care shows your commitment to your nursing staff’s well-being. Nurses who feel supported and well-staffed are likelier to stick around than those who don’t.

In 2021, 1 in 5 healthcare workers said they planned to cut back their work hours or walk away from the profession within the next 2 years.
5 Types of Nurse Staffing Models
Choosing the RIGHT staffing model of care for your facility is essential. There’s no one-size fits all model of care. The turnover rate in RN jobs is high — finding and implementing a model that fits your facility can help combat the revolving door in nursing.
Over the last 5 years, specialized RN departments had a cumulative turnover rate between 101.3% and 111.4%.

Translation — Every 5 years, these departments turn over their entire RN staff.
Nurse Staffing Model #1: Team Nursing
Team nursing is just what it sounds like — a team of nurses, including RNs, LPNs, and nursing assistants, working collaboratively to provide patient care.
An RN leads the team. That RN coordinates and delegates tasks based on patient needs and team members' skills.
The model is based on good communication, shared decision-making, and collaboration.
Team member roles and responsibilities:
RNs provide comprehensive patient assessments, develop care plans, and oversee care coordination within the team.
LPNs administer medications, perform treatments, and assist with patient care under the guidance of RNs.
Nursing assistants assist with activities of daily living, take vital signs, provide basic patient care, and support the team.
Pros and Cons of Team Nursing
Pros:
- Enhanced team collaboration and communication.
- Efficient use of resources and skills — tasks are delegated based on competencies.
- Opportunities for professional growth and skill development for all team members.
- Flexibility to adapt to changing patient needs and workload fluctuations.
Cons:
- Requires high-level coordination and communication to ensure continuity of care.
- Potential for role confusion or conflicts among team members without excellent communication.
- Maintaining consistency and continuity of care could be challenging if the team’s makeup changes frequently.
- It may require extra time for planning and coordination among all team members.
Healthcare settings where team nursing works well:
- General medical-surgical units in hospitals
- Long-term care facilities and nursing homes
- Rehab centers
- Outpatient clinics and community health centers
- Psychiatric and behavioral health units
Nurse Staffing Model #2: Primary Nursing
Again, the name says it all — A specific RN, aka the primary nurse, assumes responsibility for coordinating and delivering comprehensive care to a group of patients.
The primary nurse develops relationships with each patient, serves as the main point of contact, and collaborates with other healthcare professionals to meet patient needs.
The model emphasizes continuity, individualized care, and nurse-patient partnership.
Primary Nurse’s roles and responsibilities:
Primary Nurse establishes a trusting relationship with patients and advocates for them. They also conduct assessments, administer treatments and meds, AND develop and implement care plans. Last but not least, they provide patients with education and support.
Pros and Cons of primary nursing:
Pros:
- Continuity of care and enhanced nurse-patient relationships.
- Individualized and holistic care that considers patients' preferences and needs.
Higher patient satisfaction and engagement in their care. - Opportunities for nurses to develop specialized expertise and deepen their understanding of patient conditions.
Cons:
- Higher staffing requirements to accommodate the one-to-one nurse-patient ratio.
- Challenges in ensuring consistent scheduling of primary nurses, especially in large or busy healthcare facilities.
- Increased workload for primary nurses due to their comprehensive responsibilities.
- Potential for excessive overtime associated with the prolonged involvement of primary nurses in patient care.
Healthcare settings where primary nursing works well:
- ICUs and critical care settings
- Labor and delivery units
- Oncology and specialty clinics
- Hospice and palliative care facilities
- Home healthcare services.
Nurse Staffing Model #3: Total Patient Care
Total patient care, sometimes called Case Method Nursing, assigns 1 nurse to provide complete care for a specific patient. It’s pretty much private-duty nursing.
The nurse assumes full responsibility for assessing, planning, implementing, and evaluating all aspects of that patient.
The model emphasizes a comprehensive, holistic, personal approach to patient care.
Total patient care roles and responsibilities:
An RN is primarily responsible for 1 patient's care, including conducting assessments, developing care plans, administering meds and treatments, offering emotional support, coordinating with other healthcare professionals, and educating patients and their families.
Pros and Cons of total patient care:
Pros:
- Continuity of care with one nurse overseeing one patient's entire care journey.
- Enhanced nurse-patient relationship and personalized care.
- Efficient communication and coordination within the healthcare team.
- Opportunities for the nurse to develop an in-depth understanding of the patient's condition and needs and get to know them.
Cons:
- Significantly higher staffing requirements to accommodate the one-to-one nurse-patient ratio.
- Managing the workload and time constraints alone, especially in high-acuity settings.
- Potential for increased nursing workload and burnout due to the comprehensive nature of care.
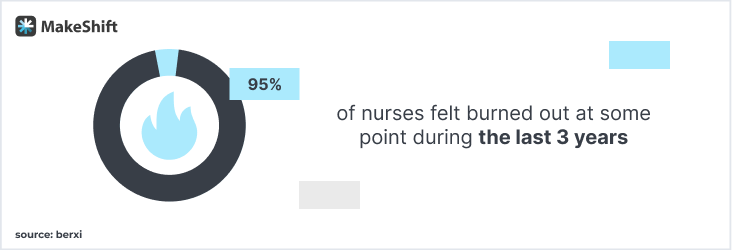
Burnout is a huge factor — 95% of nurses felt burned out at some point during the last 3 years.
Healthcare settings where total patient care works well:
- Critical care units (e.g., intensive care units, cardiac care units)
- Post-op recovery units
- NICUs
- Home healthcare settings for patients requiring ongoing care
- Rehab centers for patients undergoing comprehensive therapies
Nurse Staffing Model #4: Floating Staffing
Floating staffing refers to moving nurses from 1 unit or department to another based on fluctuating patient census or staffing needs.
The floating staff is temporarily assigned to work in an area outside of their regular unit or specialty.
The model aims to address staffing gaps and ensure adequate coverage across different areas of the healthcare facility.
4 Reasons to use floating staff:
- Patient numbers fluctuations — An unexpected surge in patient volume.
- Staffing shortages or absences — Due to time off, illnesses, or leaves of absence.
- Emergencies or critical situations — Requiring immediate extra support in specific units.
- Cross-training initiatives — To enhance nurses' skill sets and provide them with broader experience.
Pros and Cons of floating staffing:
Pros:
- Offers more flexibility and responsiveness to changing patient needs and workload demands.
- Efficient utilization of nursing resources, ensuring appropriate staffing levels in all units or departments — workforce optimization in action.
- Opportunities for professional growth and development through exposure to different patient populations and care settings.
- Enhanced teamwork and collaboration among nurses from different units or departments.
Cons:
- Challenges in adjusting to a new unit's policies, procedures, and patient population.
- Potential disruption to continuity of care and familiarity with patients.
- Higher stress and workload for floating staff due to the need to adapt on-the-fly to multiple new environments.
- Possible strain on an existing team’s dynamics + potential resistance from staff members in the receiving unit.
Healthcare settings where floating staffing works well:
- Hospitals with multiple units or departments (medical-surgical units, ICUs, and ERs).
- Large healthcare systems with centralized staffing pools that handle staffing needs across various facilities.
- Specialty areas requiring additional support during peak periods (L&D units or ORs).
- Long-term care facilities or nursing homes.
Nurse Staffing Model #5: Patient Acuity-Based Staffing
Patient acuity-based staffing determines nurse staffing levels based on the complexity of patients' medical conditions and care requirements.
This model recognizes patients' varying acuity levels, influencing the amount of nursing care and attention they need.
The goal — Match the number and skill level of nursing staff to the patient population's needs resulting in safe and effective care delivery.
3 Methods used to determine patient acuity levels:
- Assessment tools & standardized frameworks — They assign acuity scores based on patient characteristics like diagnoses, vital signs, mobility, and level of assistance required.
- Nursing staff collaboration — A collection of shift reports, discussions, and observations is used to gather info on patient needs and acuity.
- Interdisciplinary team member input — Including physicians, therapists, and case managers to assess the complexity of patients' conditions.
Pros and Cons of patient acuity-based staffing:
Pros:
- Tailored staffing to match patient needs, promoting safe and high-quality care.
- Exceptional use of nursing resources, minimizing over or understaffing situations.
- Happier nurses through manageable workloads and high-level staff support.
- Enhanced patient care because care plans are more aligned with the complexity of their conditions.
Cons:
- The need for ongoing assessment of patient acuity to determine optimal staffing levels.
- Challenges in adapting staffing levels to abrupt patient condition changes or unexpected patient numbers fluctuations.
- Potential for too much grey area in determining acuity levels. This requires ongoing education and training for nurses handling the assessment process.
- Resource and budget constraints might limit the ability to provide appropriate staffing based on patient acuity.
Healthcare settings where patient acuity-based staffing works well:
- Hospitals with specialized units (CCUs, NICUs, or oncology units).
- ERs — Patients present with assorted levels of acuity and urgency.
- Rehab centers or long-term care facilities caring for patients with complex medical or functional needs.
- Home healthcare agencies providing services to patients with a wide range of acuity levels.
- Surgical units where patient acuity varies based on the type and complexity of surgical procedures.
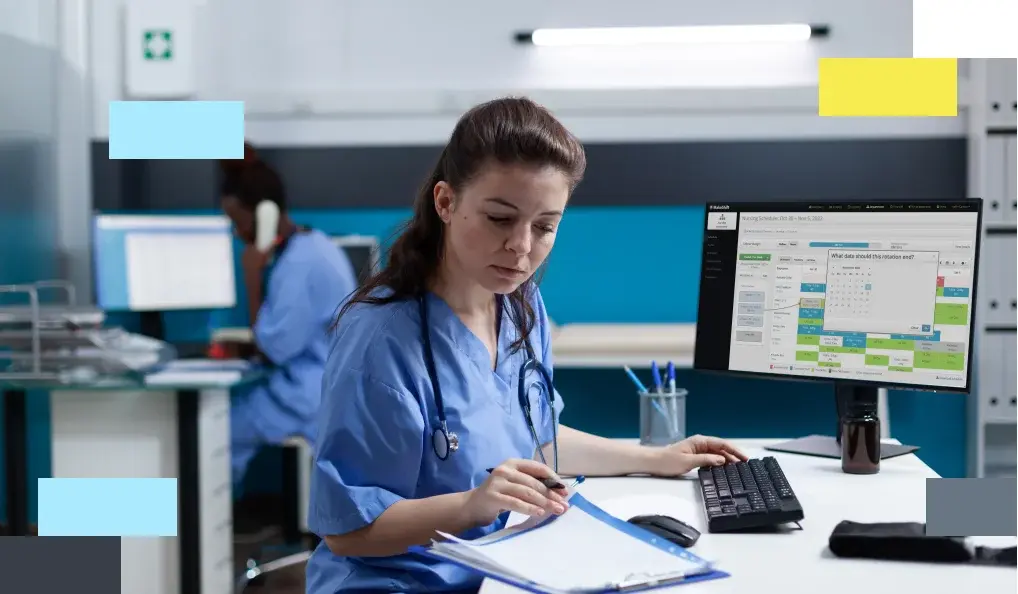
MakeShift Supports Multiple Nurse Staffing Models
We’ve got good news for you. No matter which nurse staffing model of care is the one for your facility, MakeShift is here to support you.
We get nurses on a deep level.
MakeShift was developed after our founder’s wife, a nurse, was beyond frustrated with her scheduling woes, affecting how she felt about her job.
She didn’t have easy access to her schedule and was regularly scheduled for shifts that didn’t work for her.
We’ve built a platform to support nursing managers and staff by scheduling smarter. Just like choosing the right nursing staff model will help your entire operation run smarter.
Here’s how we’ll work together:
- Integration with Nurse Staffing Models
- Customizable scheduling templates for different models
- Ability to assign roles and responsibilities based on the model's principles
- Flexibility to accommodate varying staffing ratios and patient acuity levels - Features Supporting Specific Nurse Staffing Models
- Shift swap functionality to facilitate team nursing and primary nursing models.
- Patient acuity tracking and reporting for acuity-based staffing.
- Floating pool management to assist with floating staffing.
- Comprehensive reporting and analytics to optimize total patient care.
Benefits for Nurse Managers and Staff
- Improved efficiency in creating and managing schedules, saving time and effort.
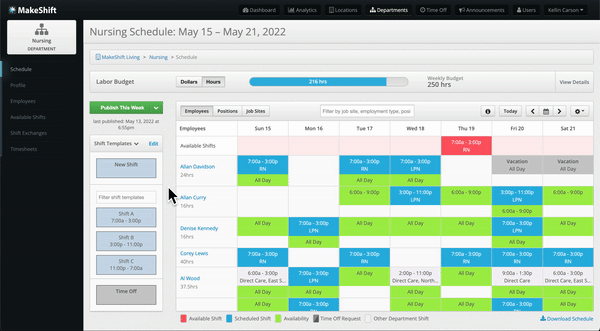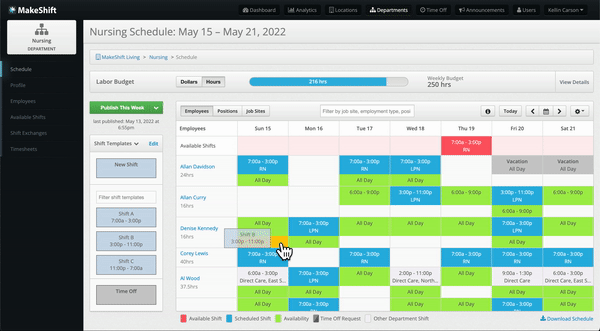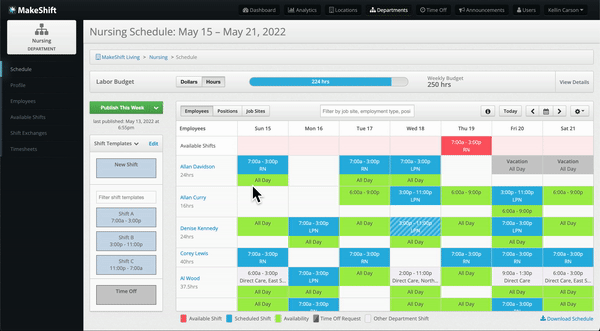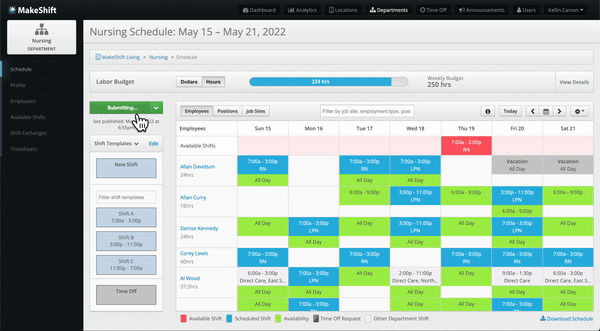
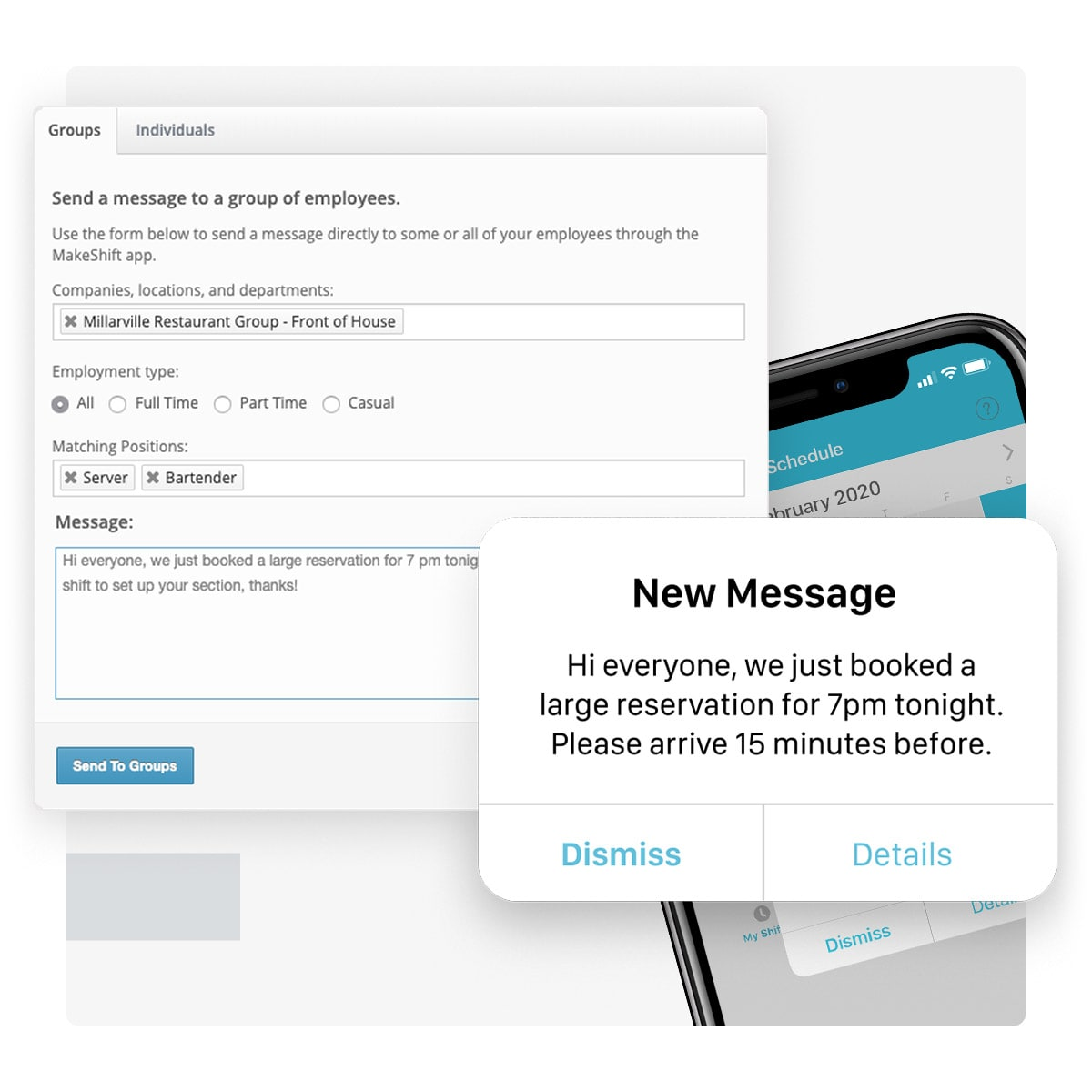
- Enhanced communication and collaboration among team members, promoting teamwork.
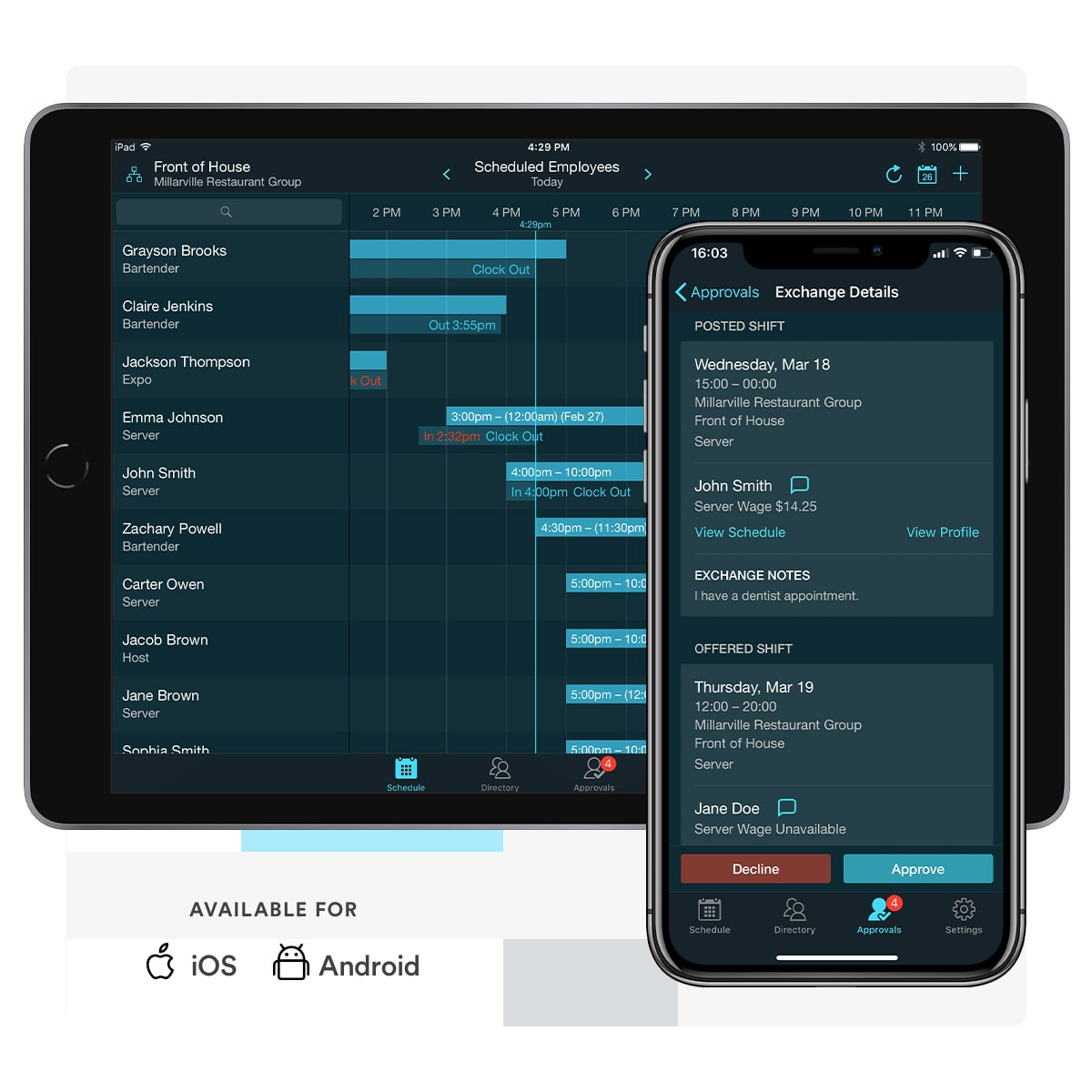
- Real-time visibility into staffing levels and gaps, so you can make necessary adjustments.
- More staff satisfaction and work-life balance through fair and transparent scheduling practices.
The Right Nursing Staff Model of Care Makes the Difference
Choose wisely when weighing the pros and cons of each nursing staff model. Take into consideration your staff, your patients, and your facility.
The correct model makes all the difference.
It’ll enhance nursing staff support, patient care, and your facilities’ operation.
Here at MakeShift, we’re ready to support you with our people-first approach to scheduling. Take a test drive and start your FREE TRIAL today.